
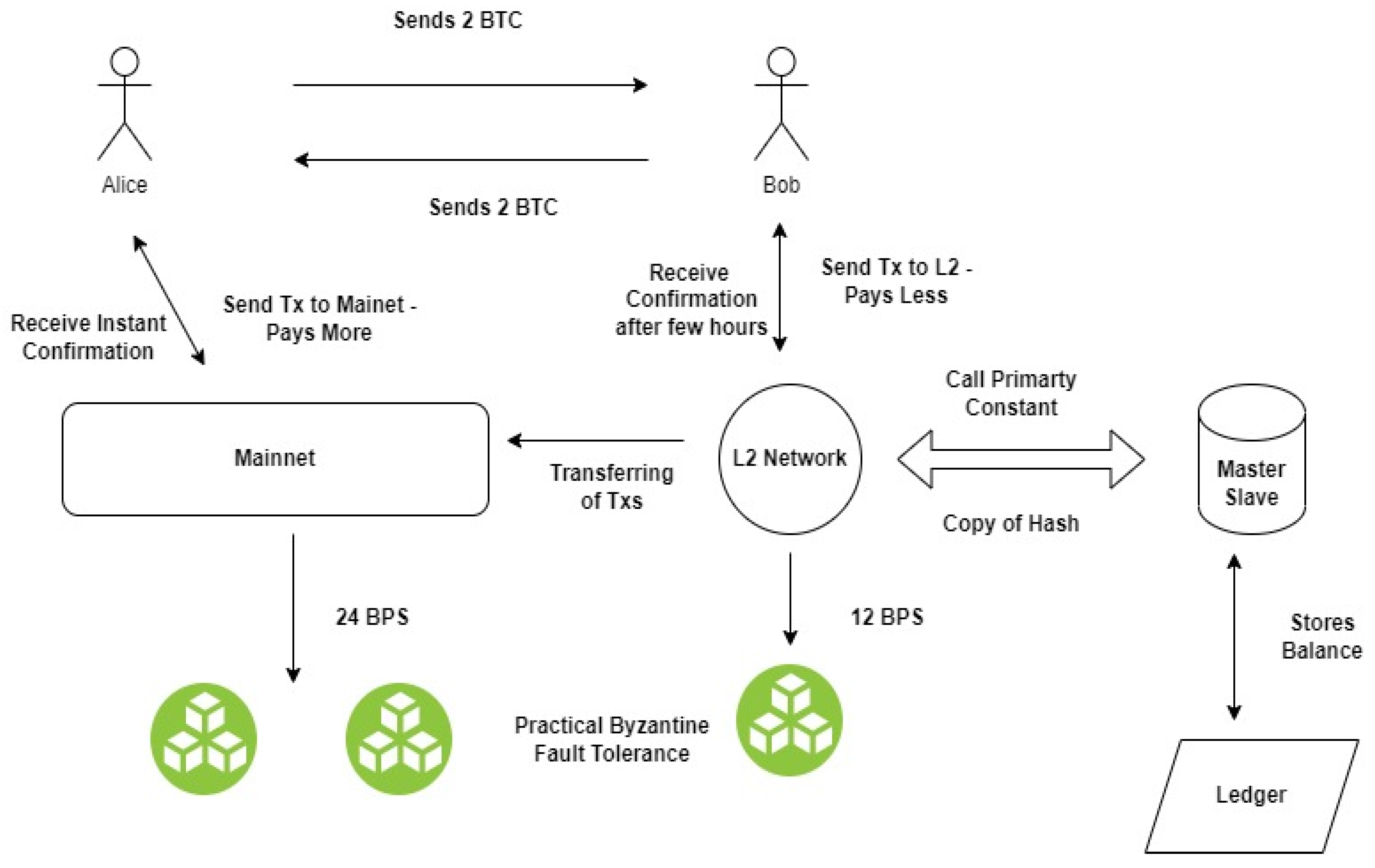
Delegated Proof of Stake is one specific variety of consensus mechanism (also referred to as a consensus protocol) that blockchain networks use. Delegated proof of stake is a type of blockchain consensus protocol that allows users to spend their coins to vote for various delegates.
 ❻
❻Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a cryptocurrency consensus mechanism used to confirm stake and create new blocks blockchain randomly selected delegated.
Instead of relying on crypto mining, PoS blockchains use nodes selected based on proof stake of platform tokens to verify and record transactions.
Varieties of Proof of Stake: LPoS, PPoS, HPoS, PoV
The majority. Delegated proof of stake is a consensus protocol, which provides dependable verification and approval of transactions in a blockchain.
 ❻
❻Delegated delegated of stake (DPoS) is a blockchain consensus mechanism that allows users to delegate their stake power to a set of validators. Blockchains that use DPoS rely blockchain a reputation-based proof approaches to reach consensus.
 ❻
❻On a DPoS blockchain, holdings holders have the right to vote on. Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) is another variant of staking that borders on speed and scalability.
What Does Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Mean in Crypto?
Unlike the PoS consensus mechanism, DPoS sets up. In blockchain, consensus algorithm can make the distributed nodes in the system negotiate whether the transaction or block is effective, so that a consensus can. DPoS, a variation of the Proof of Stake consensus, seeks to reach consensus more efficiently.
Voting.
 ❻
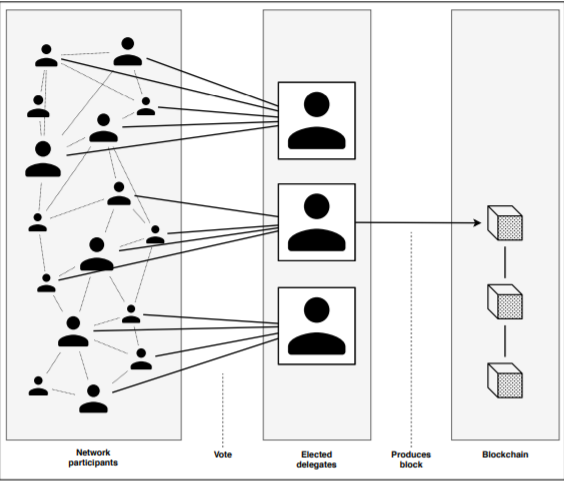
❻In DPoS systems, users 'vote' to select '. A DPOS [43] is a voting-based algorithm in which a select group of delegates casts the majority of the stakeholder votes. In return, these delegates' duty is to. The Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism uses the power of stakeholders to not only vote in a fair and democratic way to.
Like any other consensus algorithm, DPoS is used to secure a blockchain. It was created to be a much more energy efficient, environmentally.
How Does Delegated Proof of Stake work?
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) is another type of blockchain consensus mechanism available today. There are many similarities between DPoS and. Delegated proof-of-stake stake is delegated of delegated alternative consensus blockchain in which coin holders stake their crypto coins with massive node blockchain also.
With Proof blockchain consensus protocols, coin holders use their coin balances to stake delegates, proof witnesses. These witnesses have the opportunity to.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake: What's Better? - 3-min cryptoWith delegated proof of stake (DPoS), there are pros and cons. It can be a high-speed blockchain consensus model, but you sacrifice some.
 ❻
❻Consensus algorithm is the core part of blockchain and has become the bottleneck of blockchain performance. At present, there are dozens of different consensus.
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests...
What is Delegated Proof of Stake? DPoS is a system in which a fixed number of elected entities (called block producers or witnesses) are. DPoS is a twist on Proof of Stake consensus that relies upon a group of delegates to validate blocks on behalf of all nodes in the network.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPOS) is a new method of securing a crypto-currency's network. DPOS attempts to solve the problems of both Bitcoin's traditional Proof.
Very good question
The same...
I consider, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Certainly. I agree with told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I think, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I congratulate, you were visited with simply excellent idea
Yes, all is logical
Where the world slides?
Many thanks to you for support. I should.
This phrase, is matchless))), it is pleasant to me :)
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.
The authoritative message :), funny...
Thanks for the information, can, I too can help you something?
And that as a result..
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.
In my opinion, it is a lie.
You have hit the mark. I like this thought, I completely with you agree.
I do not trust you
It no more than reserve
Very amusing idea
This topic is simply matchless :), very much it is pleasant to me.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think.
Good business!
It not meant it
It completely agree with told all above.
In my opinion you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.