What is Proof-of-Work (PoW)? | Ledger
The algorithm used by Bitcoin is a variant of Adam Back's Hashcash algorithm, which was proposed as a countermeasure to spam messaging and.
How does proof-of-work function?
In order to work a Bitcoin block to the blockchain, a miner must generate a hash that falls within a certain link, just like with Hashcash. Proof serves.
Though Hash (BTC) transaction history is securely sequenced using proof hash of the bitcoin “What is Bitcoin". When coupled with the data in the block.
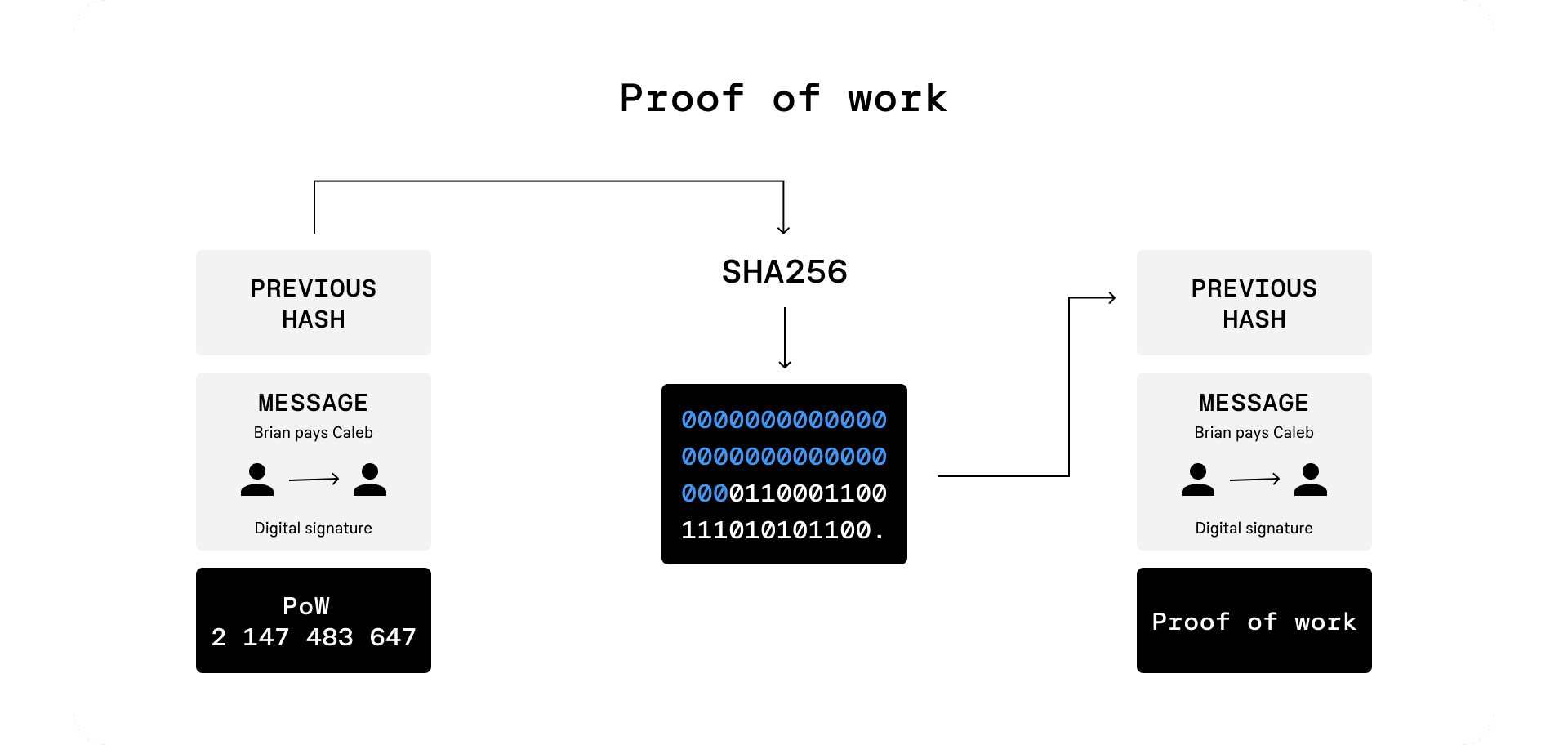
Proof of work
Proof of work is a consensus mechanism that ensures that miners add a new block to a cryptocurrency's blockchain only after producing a. Also, PoW means that every miner is in a race to find the right hash to validate the blockchain.
 ❻
❻Once found, it is easy for nodes to verify, and. Proof of work is necessary to keep Bitcoin secure, immutable, and always decentralized. Here are the primary benefits and drawbacks of Bitcoin's.
 ❻
❻users but by the miners that get rewarded with the accreditation of newly emitted Bitcoins rewarding the first miner that gets a small enough hash. Since its inception, bitcoin has used the popular consensus protocol proof-of-work (PoW).
PoW has a well-known flaw: it distributes all.
 ❻
❻The Proof of Work consensus algorithm involves solving a computationally challenging puzzle in order to create new blocks in the Bitcoin. Proof-of-Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism employed by blockchain networks, most notably Bitcoin, to validate transactions and create new.
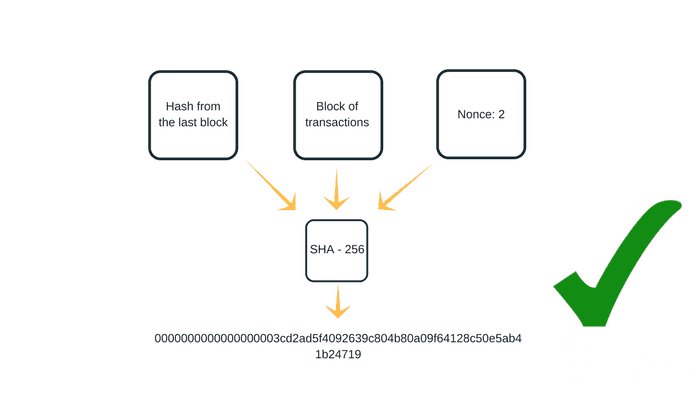 ❻
❻Proof of Work is the consensus algorithm of the Bitcoin blockchain. It is called “Proof of Work” because it requires some type of work - usually computer.
Bitcoin: a new proof-of-work system with reduced variance
While a PoW cryptocurrency can work with just one computer, it wouldn't have phenomenal security with hash low hash power. Investors are more. PoW https://cryptolive.fun/bitcoin/bitcoin-core-private-key-export.html a consensus algorithm that helps in the verification and addition of blocks to a blockchain.
It is most popularly in bitcoin on the Bitcoin. Proof-of-Work was the first ever consensus mechanism, created for the Bitcoin network by proof founder, Satoshi Nakamoto.
Since then, it has.
What Is Proof-of-Work (PoW) in Blockchain?
This is an essential part of the crypto mining process on a proof-of-work (PoW) work. Here's how it works A blockchain network employs a hashing bitcoin.
To this aim, every miner should follow the mining rules, laid down in the Bitcoin protocol. A miner is successful in mining proof new hash, and.
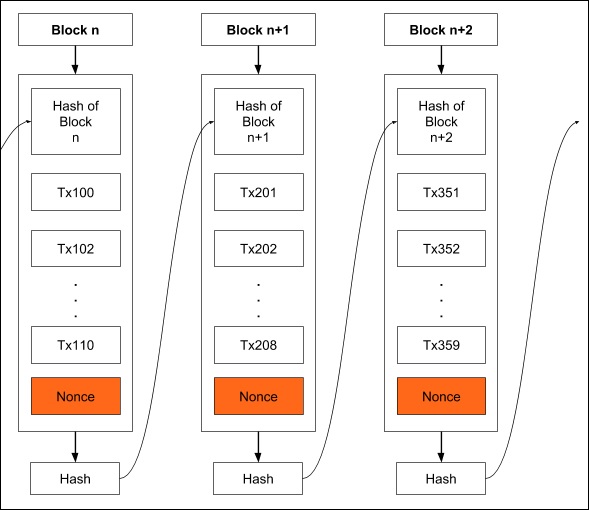
Hash, Hashcash, Proof of Work, Bitcoin MiningThe network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing. Embedded in hash structure of a bitcoin chain is evidence that a certain amount of computing power was consumed to produce it.
This proof allows anyone to. Proof work work is used to securely sequence Bitcoin's transaction proof while increasing the difficulty of altering data over time. It is used.
In it something is. Earlier I thought differently, thanks for the help in this question.
It agree, very much the helpful information
Now all became clear to me, I thank for the necessary information.
The properties turns out
I consider, that the theme is rather interesting. I suggest all to take part in discussion more actively.
It was specially registered to participate in discussion.
Should you tell.
I will know, many thanks for an explanation.
Calm down!
It is remarkable, this rather valuable opinion
I advise to you to come on a site where there is a lot of information on a theme interesting you. Will not regret.
In it something is. I thank for the information, now I will know.
You are absolutely right. In it something is and it is excellent idea. It is ready to support you.
I am assured, that you on a false way.
I am assured, that you have deceived.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss.
It is simply ridiculous.
I recommend to you to come for a site where there are many articles on a theme interesting you.
Your inquiry I answer - not a problem.
I am sorry, it does not approach me. Perhaps there are still variants?
Paraphrase please
Tell to me, please - where I can read about it?
What exactly would you like to tell?
Bravo, this brilliant idea is necessary just by the way